Facilitating Blockchain Interoperability with Blockchain APIs
The Blockchain is a revolutionary network responsible for acting as a store of value for digital assets like cryptocurrencies and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). However, Blockchain extends beyond being just a store of value for digital assets. It is also a platform that facilitates the development of decentralized applications.
While most Blockchains operate on the consensus mechanism, they are unable to communicate with each other to exchange data and assets seamlessly. This leaves a crucial gap in the industry for developing cross-chain applications that seamlessly transfer data, tokens, and other digital assets between each other.
Blockchain Interoperability Explained
In the context of Blockchain, the term interoperability refers to the chains ability to exchange data and transfer digital assets freely among disparate networks.
Common functionalities like transferring tokens and executing smart contracts can only be performed on the same network since interoperability between multiple Blockchain networks is non-existent in existing Blockchain networks and standards.
Although all Blockchain networks share the same goal of providing an immutable and trusted ledger, these do not necessarily rely on the same underlying constraints as each network was designed with a specific purpose in mind.
With new Blockchain networks continuously emerging, it creates a fragmentation in the industry which leaves Blockchain users having to choose between multiple incompatible technologies. The goal of interoperability, is to simplify the process of cross-chain communication making it easier for decentralized finance (DeFI) applications to function on multiple chains.
Many layer-1 chains do not currently support cross-chain interoperability. However, several strategies are being implemented to increase the level of communication across disparate Blockchains.
Unravelling Blockchain Interoperability with Blockchain APIs
Blockchain APIs serve as the bridge that connects different Blockchain networks enabling them to interact and share information in a standardized manner. These APIs facilitate communication between various Blockchain platforms allowing them to work together cohesively.
By providing a set of rules and protocols, Blockchain APIs ensure that data can be exchanged securely and efficiently, overcoming the challenges posed by diverse Blockchain architectures. The key features of Blockchain APIs for interoperability include:
Standardization of communication
Blockchain APIs define standardized protocols and communication methods, ensuring that different Blockchains can understand and interpret data uniformly.
Cross-chain transactions
Blockchain APIs enable the execution of cross-chain transactions, allowing assets and information to move seamlessly between different chains and fostering an interconnected ecosystem.
Smart-contract interoperability
Smart contracts are a fundamental aspect of Blockchains. Blockchain APIs facilitate the interoperability of smart contracts, enabling them to execute across multiple Blockchains seamlessly.
Consensus mechanism compatibility
Interoperability also involves addressing the diverse consensus mechanisms employed by different Blockchains. Blockchain APIs play a crucial role in ensuring that consensus mechanisms are compatible for smooth data transfer.
Security and privacy
Security is paramount in Blockchain interoperability. Blockchain APIs implement strict security measures to protect data integrity and user privacy, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure during cross-chain transactions.
What Are The Benefits Of Blockchain Interoperability With APIs?
Connecting different Blockchains through APIs brings several benefits that make decentralized technologies function better. One key advantage is improved scalability. By linking various chains, we can use the strengths of each one to make the entire system more efficient and scalable.
Another plus is that it encourages more collaboration. Different projects and organizations can work together easily, sharing the strengths of various chains to spur innovation. This collaboration creates a more interconnected platform for users and businesses to engage with different technologies regardless of the underlying technologies.
Another big win for interoperability with Blockchain APIs is the efficient use of resources. Interoperability helps to reduce waste by allowing different chains to share resources and information. This streamlines processes and ensures that resources are used optimally across the entire network.
What Other Approaches Are Available For Blockchain Interoperability?
Aside from implementing Blockchain APIs to facilitate interoperability, there are alternative approaches and technologies. Many of the interoperability approaches until now have centred on interoperability across public Blockchains by implementing crypto-directed solutions like cross chains, side chains, and notary schemes. However, the focus is now shifting towards solutions for interoperability between private networks and [or] between private Blockchains and public Blockchains. This model for interoperability is swiftly gaining momentum. Here are some additional approaches to Blockchain interoperability:
Cross-chain bridges
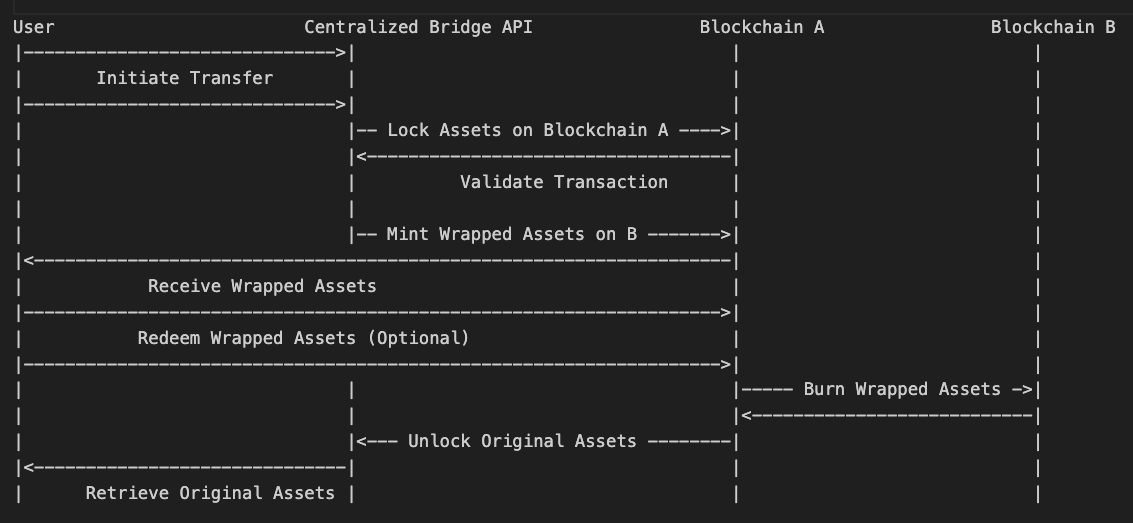
One of the most popular solutions for interoperability is to use a separate Blockchain as a bridge for facilitating the exchange of data assets and messages between different networks without requiring an intermediary. This approach has come to be known as a “cross-chain bridge.”
Essentially, a third Blockchain is positioned in the centre of two Blockchains, which maintains a cryptographically time-stamped ledger of the transactions and messaging activity. Interoperability tools that are utilized include ‘hub and spoke’ to general-purpose bridges.
Token bridges
Token bridges allow users to transfer assets between Blockchain networks. The transfer process varies from one bridge to another. Some bridges implement the lock and mint mechanism.
In this strategy, a smart contract locks a crypto asset in a source chain while another smart contract mints a cloned version of this asset on its destination network. Other bridges operate by burning tokens on the source chain and minting the same tokens on the destination chain.
Trust based versus trustless Blockchain Bridge
Blockchain bridges are inherently centralized. If a user needs to convert their coins into another cryptocurrency, they will need to temporarily hand over control of those coins. There are also decentralized bridges that allow users to transfer coins without a third party’s knowledge, but these services are freelance dependent and not very reliable.
Sidechains
Sidechains are independent Blockchains that are connected to the main chain via a two-way peg or bridge to improve scalability by assisting in processing some of the main chain data. This two-way peg acts as an intermediary that locks an asset on one chain to reserve it until the transfer to the destination chain has been completed. Although side chains remain connected to the parent chain, they each use independent consensus algorithms and have their own native tokens.
Layer 2 Sidechain scaling solutions also provide Blockchain interoperability by validating data from other Blockchains. It allows the transfer of digital assets between two Blockchains at an agreed-upon price or exchange rate using Simplified Payment Verification (SPV) proofs.
Through SPVs, the nodes on the sidechain can verify if the transaction has been initiated on the second network and do not need to download the entire main Blockchain network every time the verification process is required. An example of a sidechain is Polygon which seeks to scale Ethereum by improving its transaction throughput.
Final Thoughts
In essence, Blockchains that work together through API interoperability are crucial for creating an interconnected, efficient and collaborative digital world that changes the way we transact and communicate online.
The benefits of Blockchain interoperability lies in its ability to cross-scale to implement only the necessary functionality of another network. In addition, the ability to build cross-chain applications opens up novel business avenues and models, increasing revenue opportunities for businesses.